Over the last few years in Italy, there has been a marked growth in the amount of interest being given to the theme of family businesses (FBs) and the generational change within them. The growing attention for FBs is due to the economic boom that has distinguished post-war Italy and Europe, during which many firms have been born. These FBs are currently undergoing a generational change.
FBs are a worldwide phenomenon (Molly, Laveren, & Deloof, 2010). Over 90% of the businesses in North America, as well as the vast majority of firms worldwide, are family-owned; FB in the United States account for 78% of new job creation, 60% of the national employment and 50% of the gross domestic product. In North America (Poutziouris, 2010) and Western Europe, two of every five businesses employ two generations of family members (Ward, 2004). Approximately 35% of Fortune 500 firms are declared as “family firms” (controlled and/or managed by a family). U.S. FBs account for 49% of the gross domestic product, while Italian FBs account for 40% of the gross domestic product (Montemerlo, 2000).
In 2001, ninety-eight per cent of Italian manufacturing companies have fewer than 50 employees, yet these companies account for more than 55% of the total manufacturing workforce (Office for National Statistics, 2001). More recent studies (Cucculelli & Micucci, 2008) have highlighted that these percentages have risen to 99% and 77% for firms and employment, respectively, for businesses with fewer than 250 employees. Many of these companies either are run as family businesses or have family members as key shareholders who are capable of exerting a significant influence on company affairs.
FBs are more generally defined as firms "run and owed by a family" (Montanari, 2003, p. 5). However, there is a lack of a clear definition with regard to which elements distinguish family firms from non-family firms (Handler, 1989). In general, authors have identified criteria to calculate the degree of "familisation" of firms based on objective and subjective information (Handler, 1989). Objective information concerns the degree of involvement of the family in the property and management of the firm, the number of generations belonging to the firm, the number of male and female family members potentially involved, and the number of employees. Subjective information includes norms, values, expectations and the degree of overlap between the family and business dynamics (Montanari, 2003).
Given the difficulties in defining the phenomenon of FBs based on the variability of objective and subjective criteria, scholars have highlighted the challenge of comparing results across studies. As the literature states, studies on FBs include FBs that are very different from one another (Montemerlo & Ward, 2005), suggesting that a "chronic lack of empirical studies on the phenomenon is possible" (Montanari, 2003, p. 6). Ward (1987) defined family firms in terms of succession, including a "family business as one that will be passed on for the family's next generation to manage and control" (p. 252). Following a review of 250 articles, Chua, Chrisman, and Sharma (1999) defined FBs in terms of a business managed with the intention to pursue a vision across generations by a coalition of individuals belonging to the same family. The importance of defining what is meant by a common culture or a common vision becomes salient.
From a psychological point of view, FBs represent a social phenomenon wherein individual, family, work and cultural aspects overlap. Several studies have demonstrated that both the personality of the entrepreneur and the family model strongly characterise the business foundation. Thus, FBs represent a highly unique and relevant system that is currently affected by specific critical aspects:
-
nearly 40% of the family businesses in America and Italy will be passing the business (“passing the baton stage”, Gersick, Davis, Hampton, & Lansberg, 1997) to the next generation over the next 5 years;
-
by 2050, virtually all closely held and family-owned businesses will lose their primary owner due to death or retirement in America and Italy. Approximately $10.4 trillion of the companies' net worth will be transferred by the year 2040, with $4.8 trillion transferred in the next 20 years. Only 40% of the family-owned businesses around the globe will survive to the second generation, 12% to the third, and 3% to the fourth;
-
of all CEOs due to retire within the next 5 years, 55% have yet to choose their replacement (Gersick et al., 1997).
In Europe, the ASM-SME Observatory estimated that in the three-year period of 2001-2004, the percentage of companies involved in a generational change was 68% in 2003, 64% in 2002 and 63% in 2001.
The importance and the extent of the phenomenon of FBs has been highlighted by various European Commission directives and opinions (European Commission & Austrian Federal Ministry for Economic Affairs and Labour, 2002; European Commission, 2003, 2006) over the last ten years. These directives and opinions have focused on supporting the transition of FBs and have recommended the adoption of specific policies for this sector.
The extent of the phenomenon is also supported by additional data that highlight the low prevalence of business success across generations: Only 13% of businesses survive the third generation transition, and fewer than two-thirds do not progress to the second generation (Crescentini, 2007).
Furthermore, other studies have shown that only 5% of FBs have a successful transition (Blotnick, 1984). Only three of every ten businesses transition to the second generation, while only one in ten transition to the third generation (Kets de Vries, 1987). In Italy, 45% of employers struggle to ensure continuity. Fifty per cent of FBs reach the second generation, compared to 15% reaching the third generation and only 3-4% reaching the fourth generation (Pasqualetto, 2007).
Succession in family firms is more a process than an event (Churchill & Hatten, 1987; Farquhar, 1989; Friedman & Olk, 1987; Gilmore & McCann, 1982; Gordon & Rosen, 1981; Handler, 1990; Longenecker & Schoen, 1978; Vancil, 1987). As Handler (1994) states, "succession is not simply a single step of handing the baton; it is a multistage process that exists over time, beginning before heirs even enter the business. Furthermore, the effectiveness of succession is not limited to whether a president has been designated; the ongoing health of the firm, quality of life, and family dynamics are critical to the success of the succession process" (p. 134).
Numerous studies (Montanari, 2003; Montemerlo, 2000) by both academic and private institutions, such as banks and banking foundations, have highlighted the critical issues related to this particular phenomenon and its impact on the economy of the society at large.
One of the critical issues of FBs is the logical overlap between family and business logics (Basco & Pérez Rodríguez, 2009). It is worth considering that recent studies have suggested that inherited management within a family negatively affects the firm’s performance, due to the transfer of family conflicts to the workplace (Eddleston & Kellermanns, 2007), or a lack of management professionalism. Other studies, however, have suggested that family involvement brings significant advantages by diminishing agency problems and bringing unique resources to the family business, namely social capital resources (Chrisman, Chua, & Kellermanns, 2009; Dyer, 2006).
The heterogeneity within the group of family businesses has encouraged scholars to inquiry upon different ways to distinguish among different types of family firms (Basco & Pérez Rodríguez, 2009; Corbetta, 1995; Dyer, 2006), developing several classifications. Yet the existing set of typologies are mostly based on the amount of family involvement in ownership or management (Dekker, Lybaert, Steijvers, Depaire, & Mercken, 2013).
Dyer (1989) has highlighted the importance of family business culture to deepen the insight into these complex systems, where family and business firm merge their boundaries.
This “institutional overlap” (Lansberg, 1983) between family norms and business rules is widely recognised in the current literature. It has been defined as a common denominator across various theoretical models and analysis grids that have been created by the different subject areas involved, including jurists, economists, tax-consultants, business-studies experts, and psychologists (Boldizzoni, 1988; Gersick et al., 1997; Schillaci, 1990).
The aims of this study were to verify and explore this institutional overlap in a group of Italian family firms undergoing intergenerational succession and to assess the role played by the “family business culture” (Dyer, 1989), intended as the specific cultural traits of the whole integrated system that comprises family and family-owned, family-managed business firm.
Theoretical Frame: The Local Culture
Since the 1970s, culture has been one of the main interests of anthropology, pedagogy and sociology, resulting in several different definitions with different systems of measurement (Tosi & Pilati, 2008). Nevertheless, organisational behaviour studies have also highlighted the emergence of soft approaches in relation to the hard ones. According to Bonazzi (2002), these approaches can be distinguished into cultural approaches (Gatrell, Jenkins, & Tucker, 2001; Hofstede, 1993; Kunda, 2009; Martin 1992; Normann, 1986; Schein, 1985) and interpretive approaches based on the subjectivity of the sense-making processes (Weick, 1995).
A relevant part of contemporary psychology ranges from a socio-constructivist origin (Bruner, 1990; Harré & Gillett, 1994; Valsiner, 2009; Zittoun, Gillespie, & Cornish, 2009) to a psychodynamic approach (Salvatore, Davanzati, Potì, & Ruggieri, 2009). This distinction - between culture and interpretative approaches - is overcome, and in some ways integrated, through the concept of Local Culture, which has become recognised as a scientific construct based on its observable and measurable nature (Carli & Paniccia, 1999; Salvatore & Scotto di Carlo, 2005).
According to this perspective, family and organisational (business) dynamics are treated as expressions and consequences of the interpretations that the actors make based on their own context. They are symbolic dynamics that can be defined as Local Cultures (Carli & Paniccia, 1999). The Local Culture (LC) is a specific outcome of the co-existent processes of emotion and thought, where the first process somehow defines and restricts the second process. In other words, the LC is set up in cooperation with the unconscious (emotionality), which governs the processes of emotional categorisation, and the conscious, which controls the operational categorisation (thought) (Fornari, 1979; Matte Blanco, 1975).
How does culture work? LC can be considered a mental software that decodes information so that behaviour can be constructed. LC is a specific mental symbolic order that is object dependant and hierarchically organised. It is changed in relation to the objects with which people relate (Cesaro & Ruggieri, 2011). The adjective “Local” underline the situated nature of culture in order to its dependence on the object and target population. LC as an expression of a particular symbolic order does not imply a single thought or action of all the actors within a context. In contrast, LC allows for a plurality of cultural models in relation to the reference objects that determine different opinions, attitudes and behaviours in diverse target population.
The actors give meaning and significance to their actions recurring to shared cultural codes, which entail both cognition and emotionality (Ripamonti & Kaneklin, 2006). Every individual is influenced by the culture in which he socially positions himself. In this case, the objects being discussed are a) the family, b) the business and c) the generational change.
LC refers to a common platform that generates shared meanings. Cultural models precisely represent the ways of interpreting how the actors relate to the LC through different views, opinions and attitudes, all of which are related to the same object. Therefore, cultural models describe the variability of sense and meaning present in collective life. Identifying the cultural models active in a FB means studying the variability of the active viewpoints in that specific social dimension by tracing them back to a single shared origin: the LC. At the same time, it means understanding the decision making process and the organisational behaviour shaped by the culture models. Identifying these cultural models makes it possible to access the plurality of the emotional processuality different ways of thinking and acting in the FB.
According to this perspective, social and market change, the diffusion of innovative business practices, such as the development of adequate activity planning systems (e.g., those of the generational change), and the general systems of corporate governance are all processes linked to the family and business culture. These processes are also linked to the functions of the active role in the context under study, such as the father/founder. The cultural dimension, which includes channelling and mediating the interpretations of the environment developed by the actors, is a key variable for the development and/or maintenance of the business and a key factor that determines the success/failure of the generation change.
For family business systems, emotionality, therefore, do not need to be considered a disturbing element, as claimed by some scholars (Dyer & Handler, 1994; Montanari, 2003). On the contrary, it is a principal and essential dimension of behaviour because of its ability to give meaning and significance to human actions. It gives a meaning to reality, which in some ways is always emotional and never neutral (Salvatore & Scotto di Carlo, 2005).
The Present Study
The present study investigated the overlap of the family system with that of the business through the use of local culture. By adopting an idiographic approach (Salvatore & Valsiner, 2010) and recognising the unique psychodynamic process of FBs (Kellermanns & Eddleston 2004, 2007; Nicholson, 2008), this study aimed to identify the cultural models starting from what families define as a) family, b) business and c) the generational change. These three objects, more than other, can be considered the core elements of the connection between the individuals with the family and the business system: In fact the generational change represents the way through which the actors reinterpret the concept of family and business and direct their actions in future prospective (Björnberg & Nicholson, 2012).
Method
Participants
The participants were divided into two equal groups: that of the incumbents, or current heads of the business, mostly company founders, letting go and transferring their leading roles (Seniors), and that of the successors, in the process of establishing their role within the firm (Junior).
In total, there were 50 participants, including 25 Seniors (M = 60.5, SD = 3.5; 20 males, 5 females) and 25 Juniors (M = 29.9, SD = 4.6; 15 males, 10 females). They were selected using the snowballing technique (Morse, 1991). This technique enables the further recruitment of participants with the help of the first participants, who identify other potential participants based on their relationship networks. The industrial association in Monza indicated the companies associated with them and which companies were currently undergoing a generational change.
Given the complexity of several factors of variability in the target population (e.g., turnover, number of employees, industry sector), the sample was balanced on the basis of the following variables: company, position (Senior, Junior), gender, age, and number of employees.
The Emotional Analysis of Text
The Local Culture of the FB, with particular reference to the generational transfer, was identified using the EAT (Emotional Analysis of the Text). The EAT is a method of content analysis developed in order to explore the emergence of local cultural models characterizing the participants’ narratives in relationship with an object of investigation. It is based on a general theory of meaning and it enables the researcher to code and map the texts produced by the participants in a meaningful way. In fact, it assumes a semiotic and dialogic view of the mind, according to which people use speech to constructively interpret their experiences (Salvatore & Valsiner, 2010), in a process of intersubjective sense making. According to this view, speech assumes its meaning value in a cultural context, shaping the dialogues and the individuals’ minds at the same time.
This method belongs to a family of models focused on representing the content of a text, namely the cultural meanings it conveys. Rather like Grounded Theory (Glaser & Strauss, 1967), it starts from the text and, by mapping the text meaning content through an iterative and interpretative procedure, it comes to define a representation of the textual data in terms of thematic nuclei, or local contexts of meaning. Basically, it takes into account the specific interconnections that words create within a particular text, as well as their frequency of appearance (co-occurrence and recurrence). As a method focused on the co-occurrence of words, it pursues to highlight the “contextual effect” of the meaning of single words. In other words, the sense and the meaning do not depend on a single word but instead on the relationship between words within the text. A set of frequently co-occurring words mark a specific thematic context.
The EAT has been considered a “Text-Driven” content analysis methodology noted as “fishing expeditions” (Krippendorff, 2004, p. 340) because it does not include specific research questions and because it permits significant thematic domains to identify semantic variability of the text corpus rather than a priori categories defined by the scholar (Krippendorff, 2004).
EAT is performed using the T-Lab software (Lancia, 2000: www.tlab.it). A text is always open to many different levels of interpretation. This kind of semantic analysis reduces the multidimensionality of meaning within a text utilising semantic analysis procedures embodied in the software, which are aimed at ensuring a valid representation of the textual data. The researchers establish the statistical parameters of the analysis performed by the software and then interpret the results (the subsequent mapping of the texts as clusters of linked words) on the basis of a theory of meaning. The inferential process is applied considering the statistical link between words, the same sequence represents an associative chain that is both socially and culturally defined: It is interpreted based on the “free association” technique used in both psychoanalysis and psychodynamic theory. The relationship between words identifies the socio/emotional representation, i.e., the symbolic process that is underway. Each word acquires meaning from the previous and following terms, thereby reducing the polysemy that it bears.
EAT postulates that linguistic production is organised by two types of words: a dense word (lexemes with high polysemy valence and a high emotional communication level, e.g., “enemy”, “bad”) and a not dense word (words with a high ambiguity level and low polysemy, e.g., “which”, “however”). The lexemes (sets of words derived from the same root) have a high polysemic value that may convey, from a symbolic point of view, an infinite variety of meanings. In this sense, they are real keywords full of emotionality. Polysemy refers to the infinite emotional association of a meaning that is attributed to a word when it is set from the text corpus that reduces its polysemy.
This chain of dense words (lexemes) shows a shared affective symbolisation that is related (via Local Culture) to the object of investigation.
The principle underlying EAT is the allocation of the meaning given by the researcher to the relationship between words that belong to different classes of statements. In addition, the reliability and validity that determine the statistical power of the EAT are based on the person organising a narrative that is as clear as possible for the objects presented to him.
According to socio-constructivism prospective, this methodology is essentially a data driven methodology (Strauss & Corbin, 1990) and calls for the theoretical sensitivity of the researchers who have the task of attributing meaning to the data based on abductive logical (Hirasawa, Ki-Chul Kweon, & Learmount, 2007; Krippendorff, 2004) and on a hermeneutic/interpretive activity for understanding the data (Gelo, Braakmann, & Benetka, 2008; Krippendorff, 2004; Mannetti, 1998).
Procedure
Data were collected with the help of unstructured interviews (Corbetta, 1995). Because the distribution of the vocabulary and the co-occurrence in the vocabulary were relevant, it was important that the respondents were not guided by either predefined themes or contents or procedures for presenting the questions. Therefore, the respondents could freely organise their discourse without any subsequent form of influence.
The interviews were conducted in such a way that the respondents presented and justified their opinions in the manner they deemed the most appropriate, isolated from any noise, including communication with other family members or the company during the study. The participants interviewed were presented with the following thematic areas that included a stimulus-object for the production of discourse: Family, business and generational change. Each interview lasted between one hour and one hour and a half. The interviews were transcripted verbatim and then the relative texts united into a single textual corpus. A dictionary was created for the data analysis, and it excluded any pronouns, auxiliary verbs, conjunctions, or prepositions, as well as the words “family”, “business/company” and “generational change” due to the subject of our analysis; this dictionary was then introduced to the respondents. The manual procedure of lemmatisation was adopted to reduce each word (e.g., verbs, adjectives, nouns) to the same semantic root (lexemes) to identify the dense words.
Clusters are obtained by a statistical analysis of the multiple correspondences between the individual lexemes and text segments as well as a subsequent hierarchical factor analysis applying the Ward technique.
Each obtained cluster was a set of text segments characterised by the same lexical units (lemmas) and the most characteristic context units (sentences) from which it was composed.
The Chi-Square test (χ2) verified the significance of a word recurrence within each cluster. The lexemes subjected to the statistical analysis of the multiple and factorial correspondence had a Chi-Square test (χ2) = 11. The dendrogram tool segregated the repartition into five clusters.
Through the cluster analysis, the relationship between the cluster and the n-dimensional space that represented the latent aspect organising the core semantic oppositions of the text corpus was explored. The relationship between clusters in n-dimensional space was determined using a Value Test, a statistical measure with a threshold value that corresponds to the statistical significance (p = 0.05) and a sign (- /+) that facilitates understanding of the poles of factors detected through Correspondence Multiple Analysis.
The first step included interpreting the cluster words (known as Cultural Models - CM) that represent the culture patterns. This step was followed by interpreting the clusters (CM) in the factorial space that represents the Local Culture related to the object of investigation. The criteria of interpretation are addressed in models of affective symbolisation (Carli & Paniccia, 2002), which are derived from the primitive system of model categorisation of reality in psychodynamic theory (e.g., in/out, friend/enemy, attack/escape, in front/behind, past/future).
Results
As shown in Figure 1, the statistical analysis output is composed of five clusters.
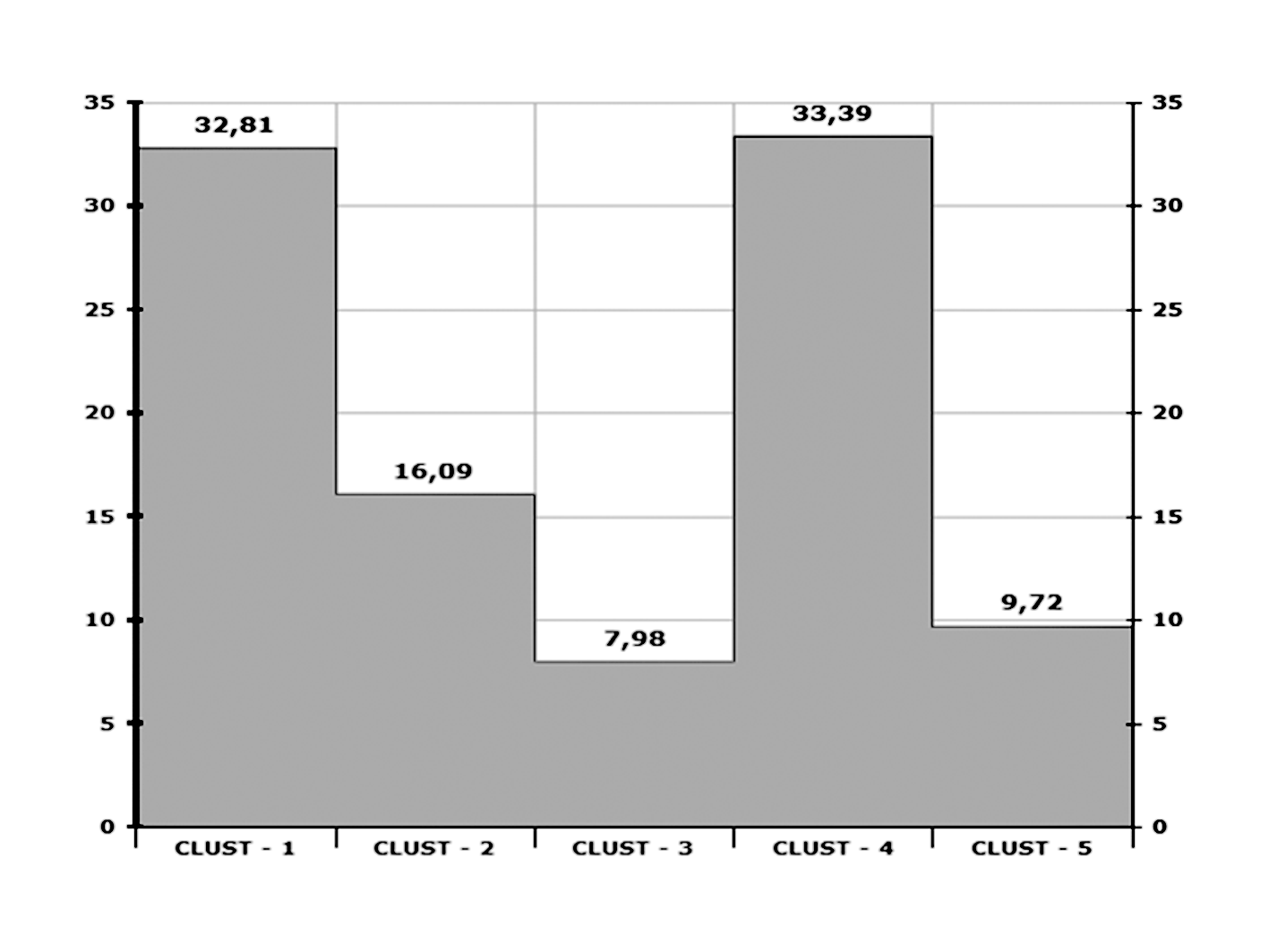
Figure 1
Histogram of clusters.
Each cluster has a different weight percentage and consists of the specific lemmas (keywords) and some examples of headlines (elementary context units) derived from the interviews.
It represents a cultural model of investigated Local Culture; they are obtained from the inferential nature of the lexemes of each cluster, excluding those with a Chi-Square (χ2) < 6.
The name of the clusters derives from the interpretative activity of data taking in account the sequence of lemmas and the use of lemma in Elementary text Units (Table 1).
Table 1
The Most Representative Lemmas and the Elementary Text Unit
| Cluster | Lemma | χ2 | Elementary Text Unit |
|---|---|---|---|
| Cluster 1 (32.8%): The gilded cage | responsibility | 46.3 | My father is responsible for production |
| role | 30.0 | My role is in administration | |
| sale | 22.7 | I’m responsible for sales | |
| future | 15.8 | I’m optimistic about the future | |
| guarantee | 12.7 | I have the responsibility to guarantee the customers | |
| Cluster 2 (16%): Impossible to wrong, impossible to innovate | study | 91.5 | I always worked and studied at the same time |
| luck | 38.1 | I was lucky | |
| excel | 23.2 | You must study to excel | |
| training | 15.1 | The training during school is different compared to the practice in the firm. | |
| university | 11.4 | I was at university. My father was not; | |
| Cluster 3 (7.9%): Innovation and CRM | service | 200.4 | We serve the customers, we produce value for customers |
| market | 142.3 | We follow the market | |
| realise | 131.4 | We realise needs for the market | |
| wealth | 126.6 | If we earn money and we produce wealth, we deserve it | |
| invent | 12.1 | First, we always try to invent something | |
| Cluster 4 (33%): Worship of the family | relationship | 58.1 | A symbiotic relationship exists between us |
| family | 30.7 | The family makes these economic results possible | |
| grow | 29.4 | I was born here; this is my second home (the firm), where I have grown | |
| faith | 20.3 | Faith in the parent is fundamental | |
| Cluster 5 (9.7%): The fight for control | enjoy | 30.4 | You enjoy using your social position |
| holidays | 29.5 | You can have an expensive holiday for enjoyment | |
| arguing | 19.4 | We are arguing | |
| interest | 21.6 | All seems fantastic from the outside, but there are conflicts of interests | |
| cousin | 12.5 | between cousins | |
| commanding | 7.5 | I want to take his role and be in command |
The threshold of the test value was (-/+) 2 (p = 0.05). The sign (-/+) indicates the factorial pole with which each cluster is associated.
The illustrative variables (company, Senior/Junior, gender, age, number of employees) were not significantly different. They are not included in any clusters, as shown in Table 1.
The words in italics are the lexemes of these five groups. The statistical criterion of greatness was used, where the cluster associated with the highest percentage had a greater weight in the definition of the factorial plane, up to level 6.
The Cultural Models of Family Business
Worship of the Family (Cluster 4, 33%)
The first words are relationship and family, followed by growth and crisis. Family represents the place where relationships, in terms of conflicts and comparisons, take place. These comparisons present difficulties and can undermine the family itself, especially when the family is faced with the prospect of change due to the growth of its structure in relation to the original nucleus.
However, the crisis is a moment where choices need to be considered and decisions need to be made. Nevertheless, these choices can only be based on the concept of family that is similar to that of worship, which is related to faith (i.e., a “belief”), which has its roots in personal authority or conviction.
This fideistic dimension of the family is configured as a primary emotional core that gives meaning to action. This code determines how emotional choices and decisions are made. The main idea is based on a mental equation for which the business is the family and the family is the business. This identity is based upon the worship of the family and the business in its original set-up. Whoever works in the business, such as the employees, addresses the founders of the family (parents) as if they were their children. Both groups are in a subordinate dimension, according to a top-down logic.
The founders play their role and tend to concentrate on the decision-making processes. They are still in doubt, a condition of uncertain willingness to delegate (connect, colleagues from the Latin cum legare) the succession to their children. These children are increasingly seen as children, as if they do not have the right tools to understand and manage their lives because they lack the necessary knowledge, regardless of age or experience.
In this perspective, the identity "family = business" is maintained and reinforced by the fideistic connotations, within which the feelings of fear and negativity generated by family ties are experienced. The business is where family ties are discussed based on company performance and how business works. However, these links are maintained exactly the same in their initial set-up and are not modified based on the previously discussed identity, which is nurtured, sustained and nourished by faith in the family.
There is therefore hope that everything stays as it is and that there is no future solution of continuity, devoid of any possible element breaking away from the past. Thus, the generational change is seen and interpreted as maintaining the status quo or, rather, the status quo ante. Discussion of generational change means to shape a figure, leaving a clear and indelible mark (influence) that perpetuates such a way of thinking. This represents a clear advantage (benefit) given that different people are sharing risks and responsibilities (involve) that are grouped together (oblige), similar to a family, around the religion of sales.
In this way, the future is ensured (influence). Explicitly, the continued existence of both the family and the business is always understood in terms of the present conditions without any changes. According to this logic, the company and family systems seem to be intertwined and therefore closed and highly complicated. However, these systems represent something that should be made sacred (sacrifice) from their tiring and daily sharing of interests and difficulty.
From this perspective, the subjects involved in this cultural model do not work to live but live to work, with the FB becoming the organising element upon which their existence is based. The environmental variability is not a useful element in the definition of business processes. In contrast, what counts is the preservation of the current dynamics.
The Gilded Cage (Cluster 1, 32.8%)
The first words are occupy and weigh, followed by pass and role. Their existence is characterised by a regular commitment (being busy) as the basic premise that makes it possible to consider the possibility of leaving (pass) someone else inside the business to play a role. However, the word role refers to an organisational behaviour from action that is well-defined and limited and is a demonstration of a dynamism, i.e., the ability to uptake and move with a certain speed. However, this capacity remains constrained and inscribed and is always subordinate, which is typical of an employee/worker.
This model lacks independence because it is bound by family law and therefore to the figures in power, which makes it possible to hold together the various elements of the business reality through a dimension of control that limits the actions of others. This process guarantees the possibility to build something that is clearly observed in practical (possible) sales policies (sell).
It is thus plausible to object to (call) and then follow the difficult generational change, because implementing this generational change made the company's entrepreneurial capacity subordinate to others. It is not the result of clear criteria, such as experience, managerial competence or merit, but rather submission to the laws of the family through an obvious condition of dependency. It is not possible to proceed in any other way. This type of affective code highlights that it is useless to acquire experience and do anything different from the business. The most important thing is the close relationship with and dependence on the founder.
Based on this logic, this model is assigned to the same species (generations) according to an allocation criteria (distribute), with management activity (direct) looking to the future in terms of realising a superior condition of material advantage as the only condition to be able to go on (proceed), always ensuring that the old is never left abandoned, regardless of the socio-economic and market conditions. There have not been any regenerating systems of these processes as changes of the core business elements.
Commerce is the only ground where it is possible to think differently, where opposing ideas can “clash” and where behaviours that differ from the traditional family and business ones (history) can be implemented. Commerce, therefore, is the place where it becomes important to choose the project that counts, e.g., that makes the most profit and enables the company to produce and compete on a global scale (world). The transition from artisan to industry is not easy and requires increased responsibility according to the roles that are covered. The roles are never limited to the business but are also within the family.
As the business grows, so does the dependency of the family, which continues to become intertwined, thus forming a golden cage. It is called a cage because the family constraints are always associated with the business, and this cage is golden because one component is the livelihood of the other component.
Impossible to Go Wrong, Impossible to Innovate (Cluster 2, 16%)
The first words are study, return, luck, and home. This cluster addresses love and dedication to learning something useful outside the rules of the home to find themselves by chance (luck) in the same place of departure through the rediscovery of belonging to a family, a home (home) and a specific economic status (luck).
In this way, you begin to pay off your debt to your parents by handling an obligation or a duty (reply) or by excelling at all costs over everyone, constantly competing. However, this means accepting the differences and, therefore, setting aside any unnecessary, discordant and conflicting points of view. This also means to marry and recognise the reasons, practices and rules to follow (technique), as well as the procedures that are well established and have been in operation for years with which the family has organised itself and its work activities.
This affective code highlights how “leaving the house”, in its iconic and symbolic dimension, is something that never really happens. It implies staying at home after having left because there is neither a change expected from the family system nor any degree of renewal. In fact, “leaving the house” means staying in touch (proximity, telephone) with its own membership system. Outside the walls of the house, mistakes can also be made as long as they are conceived as a training tool capable of preparing for the future; for example, school, high-school and university programs represent educational systems where it is possible to practice some notions that may be useful for future activities.
Making mistakes is therefore limited to training, where it is also possible to practice new notions. However, they are not allowed into the home. The way to avoid them is to follow the established rules, which are the measures set by previous generations.
This maintains, albeit with some lack, the position acquired by the family (luck), by starting to follow the business through the activities of administration. Even in this case, to maintain seems to be an important dimension in keeping and organising both the family and the business relationships. It comes down to maintaining the economic and social position, similar to the market share.
The latter activity is not an easy one. On the contrary, it is full of fighting to support (struggle), especially in relation to the staff, to whom it is possible to do wrong (do wrong). Staff who have knowledge of business trends and therefore all types of conflict (war) that occur during work activities and are not an obstacle to happiness but are instead a necessary condition to be able to reach happiness.
Developing one’s own opinions and deciding which business management support method to adopt does not safeguard against any worries that something important may have been left out or something irrelevant (put) chosen. In this case, all that remains is to anticipate a consultancy capable of offering a more accurate diagnosis for the survival (lasting) of the business and the need for the security of the property.
The Fight for Control (Cluster 5, 9.7%)
The first words are boy, friend, soul and enjoy. This cluster addresses a child or an individual who is not an adult and is therefore still involved in minor business activities. It is a friend or a benevolent person with specific favourable qualities and characteristics (soul) that make it possible to take advantage of economic conditions (enjoy), thus satisfying the needs of vacation, as in the case of wives.
These are the people with whom sociality is lived and organised through meetings and conflicts originating from exchange. In fact, exchange is defined as taking something for something else. It assumes both the supplying of goods or services in exchange for another good or service and the mistaken identification of a person or object for another. Therefore, in some cases, these exchanges are both carriers of information and disagreements that may cause closure in relationships with other family members (close). This element becomes visible in the educational process (educate) of their children and emerges when different personal interests that are different world views are visible in the conceptions of life and in business management.
These are the distances that produce arguments (arguing). Distances are identified as the defects of others with whom we have a relationship, whether it is a child, parent, wife or cousin. When under these conditions, a strong foundation (base) is needed, i.e., to make decisions that have a starting point and final aim based on the interests of the business (company). At times, it is necessary to block the path of a relative who thinks otherwise (cousin). It may be necessary to equip yourself with good will and make your own way of thinking, vision, and love for the business clear to everyone, including employees.
Therefore, saving the business (business) means destroying the hostile relative (brother-in-law) and beating him, though this is a source of sorrow and conflict. There is no possibility of avoiding this family conflict because the family’s own future, as well as that of the company, is at stake. It is therefore necessary to acquire the space to command, thereby acquiring a lot of patience and the knowledge that whoever has the role of the employer is the subject of envy (envy). In fact, this can be fun, taking actions that are outside the normal canonical rules that all others are bound to obey. The actions of the employer acquire their own specific weight, by being able to determine an inevitable effect on the fortunes of the company, its employees and other family members.
Innovation and Customer Relationship Management (CRM) (Cluster 3, 7.9%)
The first words are serve, market, achieve and wealth. It seems evident that the origin of this cultural model is entirely based on the reasons of the business. Through a total dedication (serve) that is capable of satisfying any function or need (market), it is possible to actually achieve (achieve) the desired aim of wealth.
This activity requires a total dependence on the needs of the market. It must therefore determine and constantly monitor the needs of the market, so it can provide tools that will meet (support) the various needs, depending on the market sector it addresses. It must take the correct direction and trust the abilities of others to recognise the social values and merits of their work (honour) and, thus, of their own identity and family business. This recognition is finalised with the request of a contract (order). In this cluster, the culture of merit prevails.
There is a need to be consistent and motivated (persevere) and to accept some sacrifices (compromise) with several incomplete or not fully satisfactory solutions by putting aside feelings (pride) that can somehow appear excessive and unilaterally related to their personality or family and as such, altering the social relations relevant to the business. Otherwise, there is a risk of creating isolated positions in the dense web of social and commercial relationships with obvious negative effects on both the business and the “good name” of the family.
In contrast, there is a need to assess and consider the customer, as well as the competition, by evaluating with care what the customer needs and the various offers of different competitors. This is done to invest in something solid (money) that makes this assessment simple and easy, which is unnecessary for the sale due to the correct set up of the definition of the product.
This process still requires effort (cost) and having to address the risks and sacrifices that can influence a new activity (invent), as well as the return in supplying goods and services to customers. Thus, succession is an innovative activity (innovate) made possible (exist), which reflects the professionalism of the history of the business and boasts (boast) a certain aggressiveness (nastiness) in taking risks by immediately predicting market shares and exposing itself and its actions to others.
Clusters and Factorial Space
The cluster analysis indicated three latent dimensions that organised the semantic opposition in the textual corpus. These dimensions show the position of the clusters in factorial space.
The results of the V-Test (Table 2) indicated significant differences for the following:
-
Factor 1, for Clusters 5 (χ2 - 29.68), 4 (χ2 - 23.10) and 2 (χ2 - 10.23) for the negative polarity and Clusters 1 (χ2 + 34.66) and 3 (χ2 + 26.14) for the positive polarity;
-
Factor 2, for Clusters 3 (χ2 - 30.75), 2 (χ2 - 19.01) and 5 (χ2 - 12.18) for the negative polarity and Clusters 1 (χ2 + 22.42) and 4 (χ2 + 17.74) for the positive polarity;
-
Factor 3, for Clusters 4 (χ2 - 20.86) and 3 (χ2 - 17.87) on the negative polarity and Clusters 2 (χ2 + 29.33) and 1 (χ2 + 10.77). In contrast, Cluster 5 (χ2 - 4.09) was not significant.
The threshold of the test value was (-/+) 2 (p = 0.05). The sign (-/+) indicates the factorial pole with which each cluster was associated.
Table 2
Clusters and Factors
| Cluster | Factor 1 | Factor 2 | Factor 3 |
|---|---|---|---|
| Family/Market | Past/Future | Tradition/Innovation | |
| Cl.1 The gilded cage | + 34.67 | + 22.42 | + 10.77 |
| Cl.2 Impossible to go wrong, impossible to innovate | - 10.23 | - 19.01 | + 29.33 |
| Cl.3 Innovation and CRM | + 26.14 | - 30.75 | + 17.87 |
| Cl.4 Worship of the family | -23.10 | + 17.74 | -20.86 |
| Cl.5 The fight for control | - 29.68 | - 12.18 | - 4.089 |
Combining the data from the relative individual clusters and accounting for their different contrasts on the factorial plane, it is possible to infer other types of actions that define specific management business and family relationships systems. The completeness of the information contained on the factorial plane, which can be defined as a cultural space, also makes it possible to understand the ways in which the generational change takes shape and is carried out. In other words, the cultural space shows the Local Culture, that is the difference of positioning of each cultural model and the culture dynamic active.
The Cartesian axes intersect on the zero point and, moving away from it, generate values in opposite directions. Therefore, the factorial plane x, y, z is organised on bipolar dimensions for all factors (1, 2, 3). Looking at the distribution of the clusters and considering Cluster 4 – Worship of the family (Figure 2) due to its greater statistical power, one can observe that it lies almost in a central location within quadrant D. In contrast, quadrant A shows the presence of Cluster 1 – The gilded cage, which also has a central location. Together, these two clusters overwhelm the positive semi-axis of Factor 2 in quadrants A and D. They also share a fundamental dimension that is associated with family history, the past. In Cluster 4, the generational change is something that takes shape in maintaining the status quo, while in Cluster 1, some degree of change is expected, but only in commerce policy, because everything else must remain bound to the existing set-up of the family and business systems.
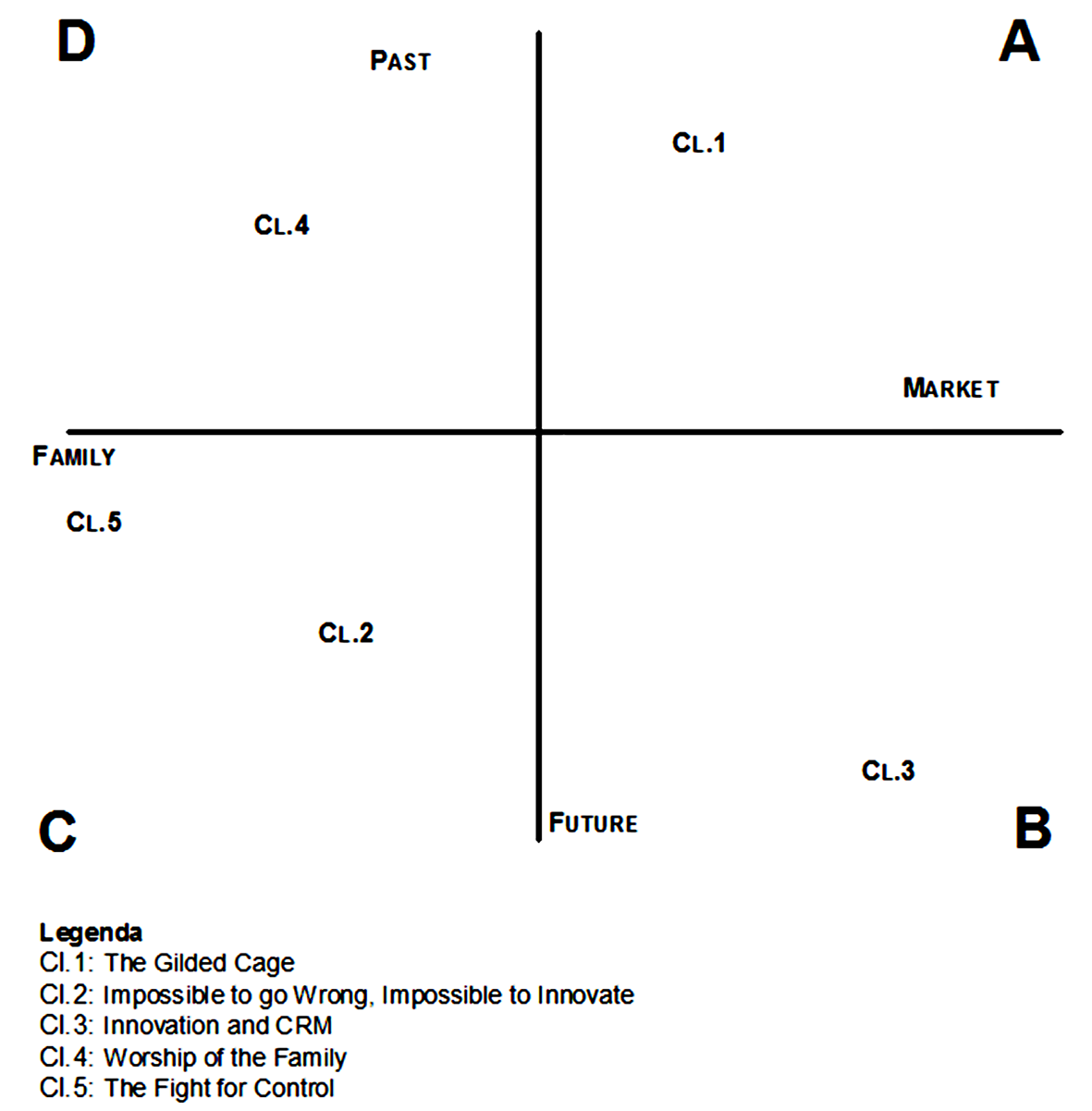
Figure 2
Representation of the X-Y Plane.
In opposition to the past dimension is that of the future. Therefore, Factor 2 is characterised by the polarity of the Past/Future.
Factor 1 is represented by the x-axis (Figure 2 and Figure 3) and acquires meaning on its negative polarity through the lexemes boy, friend, wife, and parent and on the positive polarity through lexemes such as market, serve, achieve, and produce. A first polarity seems to distinguish between the cultures of the FB and finds its definition in the conflict between Family and Market (Figure 2 and Figure 3). This polarity is confirmed by the cultural patterns in the different quadrants. In fact, quadrant C is characterised by two cultural models: Cluster 5 (The Struggle for Control), which is where the future finds significance through a non-peaceful resolution of family conflicts, and Cluster 2 (impossible to go wrong, impossible to innovate), which concerns the future in relation to the ability to maintain the position reached. Lumpkin, Martin, and Vaughn (2008) suggest that FBs “have highest potential for interpersonal conflict” (p. 135) in both substantive (disagreement about tasks) and affective terms (negative emotion between members of the family). In general, the literature suggests that these types of physiological conflict need to be managed by the founder during the generational change (Guetzkow & Gyr, 1954; Karofsky et al., 2001; Lumpkin et al., 2008; Nicholson, 2008). In fact, such conflicts can generate diseconomies.

Figure 3
Representation of the X-Z Plane.
Figure 2 clearly includes the detailed dynamic between the different cultural models in the semi-axis (past) in quadrants A and D. They interact and organise their lives based on the family. The family is the dimension, or the generative nucleus used to make business choices. In addition, the family logics are characterised by size, which privileges the dynamics of the in-group rather than those of the out-group. These culture patterns shape any form of thought and behaviour according to the relevance of the interlocutors, e.g., the advice received in relation to the internal/external dynamics. Everything that is outside the family system does not belong to the pattern and is therefore seen as alien, provocative, or an enemy to be resisted.
Keeping in mind the negative and positive aspects, Pearson, Carr, and Shaw (2008) warned of the operating mode in FB. They proposed a Familiness construct theory to explain the different logic between family firms and non-family firms, noting that family represents both a constraint and an opportunity in terms of social capital. Royer, Simons, Boyd, and Rafferty (2008) discussed “nepotism” actions for the logic of self-referential systems, which are actions that do not involve a change or assimilation of information other than those existing within the family history or place of life. Internal successors are preferred to external (idem). It is thus impossible to use any information learned externally (Cluster 2) because on the outside, the rules of the game differ from those of family and everything must be kept as is (Clusters 1, 2, 5). The only possible change is at the top of the system. The motivation that distinguishes these types of behaviour is affiliated for Clusters 1 and 2 and power for Cluster 5 (McClelland, 1985).
As discussed by Montemerlo (2000), these cultures find expression in their inability to use a consultant who is not recognised as a member of the family or as someone who has worked for years with them and is thus unable to understand the family's business processes, such as market logics. According to these cultures, there is no room for information coming from a person who does not frequent the family and the business regularly (e.g., on a daily basis over the course of years). These aspects are more characteristic of the Italian FB than the American FB phenomena (Montemerlo, 2000), due to the different background linked to the conception of family (Zattoni & Ravasi, 2000).
Some management models do not take much account of the environmental variability to which a business is subject and tend to organise their business processes based on mechanical models rather than organic ones (Tosi & Pilati, 2008).
In contrast, Clusters 1 and 3 in quadrants A and B interact with each other through the market. They are cultures where the business organises the processes and activities, highlighting how they have varying degrees of openness to the outside and are therefore capable of seizing the business opportunities in the market, though they contrast each other. However, due to its anchorage to the family history, Cluster 1 fails to learn and acquire the exploratory capacity that is the very characteristic of the cultural model of Cluster 3, where the motivation for success (McClelland, 1985) promotes the development of the use of any information, regardless of the family system to which it belongs.
Considering the positioning of the clusters in relation to the third factor (Figure 3), the data confirm that quadrant B represents the size of this development within the local culture in question. In fact, the quadrant B applies logics that allow for the existence of merit-based systems through monitoring of the management of the business. It is a control that primarily comes from the market and, therefore, the customer. This new factorial distribution also makes it possible to see how Cluster 1 (The Golden Cage) is again a way in which family tradition meets the market. However, quadrants A and B (Figure 3) highlight several interesting differences.
The innovation of the business process necessarily entails abandoning family traditions because of customer needs. It is worth noting a further element of difference in the ways of relating to the market between the cultures of Clusters 1 and 3. While it is not possible to discuss specific production aspects in cultural model 1, it is completely possible in the third model. In fact, it is necessary to start from production aspects. To better understand this difference, the businesses working with the cultural model of the golden cage never question their relationship with the suppliers and vendors with which it has established a relationship of trust, even in light of cost. This is considered acceptable due to the assumed “familiar” relationship that has been acquired. Moreover, respect for tradition does not allow questioning this relationship. However, doing so does open up new possibilities while maintaining some traditional aspects. Thus, it becomes possible to think of opening up new sales channels through the use of technological tools (e.g., web, mobile phone), while keeping as much as possible unchanged.
In contrast, the dominant element that organises Cluster 3 (Innovation and CRM) is the ability to intercept new markets or old markets that require new ways of defining the product and service.
In panel D, tradition and family are still the organisers of the sense through which the generational change occurs and are replacements for the vertices that do not require substantial changes (Cluster 2 Impossible to go wrong, Impossible to innovate). In summary, this type of action may use the following statement: “If you do not change, you cannot go wrong”.
In addition, an analysis of the factorial plane X-Z highlights a highly significant and critical issue through the position of Cluster 4 (Worship of the family) in quadrant C. A first interpretation appears to show some inconsistency in the data that would call into question its validity and reliability. It raises the question of how it is possible that this cultural model is between Innovation and the Family.
As supported and discussed in the description of the cluster and in the previously mentioned considerations, it is evident that the cultural model of the worship of the family is not the carrier of innovative culture but is instead far from it. The EAT literature defined this output as a rare case where it is possible to understand the symbolic variation of emotional issues, such as the family and the business. In this case, we are confronted with ambivalence and ambiguous aspects of the culture (Carli & Paniccia, 2002). This cultural model highlights how it considers families and business owners who say that innovation processes are very important for the development of their company. They speak of hypothetical realities that are organised as a rhetorical procedure, devoid of any active foundation. Their behaviour is similar to those who attend conferences to meet people rather than in response to an interest in the subject. Those attending conferences on family businesses consider that the speakers have nothing to teach them. This phenomenon is also due to the Italian proverb: “don't air your dirty laundry in public”.
This element discusses a more critical issue that is associated with the intervention in or planning of preventive actions for a successful generational change. It is clear how this logic denies any action, sign, or information of support derived from consultants.
Finally, the explanatory variables (company, position (Senior, Junior), gender, age, number of employees) considered were not statistically significant, with the exception of those identifying the businesses, which were omitted for reasons of privacy.
The lack of cultural differences between Juniors and Seniors can be explained by the theoretical model used. The culture of the family business, as been studied here, is unlike any other social condition for which the family dimension does not coincide with the work dimension: it is less susceptible to semiotic stress. It is also less susceptible to symbolic changes. Because fathers and children are involved in the cultural processuality, a lack of cultural diversity between their positions can be expected. This is known as the Intergenerational Influence effect in FB research. By adopting a different theoretical approach, i.e., the Symbolic Interactionism and Theory of Planned Behaviour, Carr, and Sequeira (2007) confirmed that parental work experience may have significant effects on children and that these effects can be internalised as norms of behaviour within these children in the future, thereby shaping the entrepreneurial intent of the successor. This strong relationship between the founder and successor explains the lack of statistical significance observed for the other variables. In fact, the individuated cultural models are so shared among the participants that no variables become discriminating. The “company” variable only discriminates the cultural models. In other words, each company is characterised by its organisational culture, as demonstrated using the organisational theory (Schein, 2000; Weick, 1995). Social and cultural vicinity are also considered as good circumstances for the conveyance of skills and competence (Ripamonti & Scaratti, 2012), as from senior to junior members within the family business.
Conclusion
The aim of this study was to verify the overlap between family and business. Our results confirm the existence of different culture models of the family business, which influence the action taken in the course of the intergenerational transition process. We see family, family managed business and ownership as a whole integrated system, wherein the same actors play their role referring to a shared symbolic order (Local Culture, as defined), which entails both cognitive and affective direction. The Local Culture show many different kinds of symbolic repertoires and approaches to the intergenerational transition. They are expression of different levels of connection with the general social and economic context. In some cases (Worship of the family, The golden cage, The fight for control) there is a marked retreat on the familiar symbolic order, heritage and the web of relationships within the family take the leading role, while the gradual building of the successors’ leadership and skills (Salvato & Corbetta, 2013) are less represented. In other cases (Impossible to wrong; Innovation and customer relationship management), there is ample representation of the business context and of relationships outside the family circle (even if it tends to present itself as preoccupation). Basically, our research highlight the existence of two kind of passing of baton: focused on family/tradition and focused on market/innovation.
As demonstrated by this work, the generational change is a transition of the entire family organisation rather than a simple rotation (Handler, 1994). It urges researchers to compare all parties through the structuring of a new symbolic order, e.g., a new culture capable of capturing and using the signs of change within the family and outside. In this perspective, a generational change in business means addressing issues of co-existence between the family generations, which includes tools and other devices, in relation to a generational change confined to the single dimension of succession.
Limitations and Future Research Directions
This study is not without limitations. First, as discussed previously, the literature on family businesses is of a different nature (e.g., economy, organisation, financial, legal studies). Unfortunately, it was impossible to access other variables, such as annual turnover, sales indicators, and financial and market indicators (Kaslow, 2006). We may have been able to better understand the relationship between cultural patterns of FBs and their origin by comparing these variables with our results. However, the involved firms denied access to these data because they were considered confidential and sensitive information.
Second, the firms are not homogenous in many aspects. We focused on firms in generational change, thereby reducing variability through the building of a macro category; however, the variability was maintained as a critical dimension of FB studies according to the methodology of the research (Montemerlo & Ward, 2005).
Third, other aspects related to individual differences, such as personality, leadership, locus of control, self-esteem, and self-efficacy (Gorrese & Ruggieri 2012, 2013; Lumpkin et al., 2008), could be more informative about the Local Culture. We did not find studies that crossed individual differences and culture variables in FBs, e.g., the influence of individual differences on family dynamics.
The approach in this study highlights the value of the family dimension and has the advantage of identifying the intersubjective depth that distinguishes these types of families. It also highlights how the dynamics of families and businesses should be considered with a different lens according to the context in which the psychological aspects take shape and meaning through the contingency by which the phenomenon occurs. The proposed methodology (ETA) allows us to identify the developmental dimension present in the Local Culture. As discussed, it includes Clusters 3 and 1 in factorial space x-z (Figure 3). Thus, the generation change can be read as the transition between a culture model to another one (i.e., from Cluster 4 to Cluster 3). From an individual perspective, the generational change or passing of the baton could be considered an identity transition phenomenon between senior and junior (Ruggieri & Pecoraro, in press). Future research should focus on these issues. For example, the construction of family orientation (in terms of trust, tradition, loyalty, equality and inclusiveness values) and its variation in time could be useful in understanding its relationship with the market (Lumpkin et al., 2008).
To our knowledge, only one paper discusses generational change as an identity transition. In that paper, two clinical cases with a depressive diagnosis were subjected to a clinical intervention. The result of the treatment was the resolution of the transition from the father to the individual’s own rules of life with consequential changes in the rules of business. These entrepreneurs were unable to generate a change in their businesses because of their respect for the father’s values and family tradition (Carli, 2008).
Future studies should use a longitudinal research design to incorporate process variables more than static variables.
 This is an open access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons
Attribution License (
This is an open access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons
Attribution License (